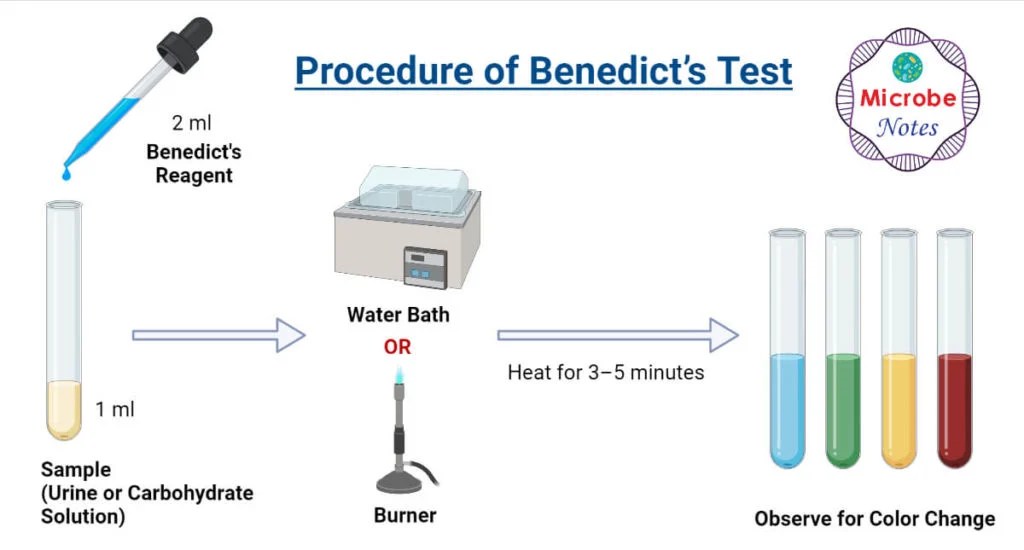
A Positive Benedict's Test Appears As
A Positive Benedict's Test Appears As - Any color change from blue to green, yellow, orange or red within 3 minutes indicates a positive benedict test, i.e. Benedict's test benedict's test is a simple biochemical reaction to detect the presence of reducing sugars. A) fructose b) glucose c) starch d) sucrose e) lactose 4. Benedict's test is used to test for simple carbohydrates, which have reducing properties. This precipitate is formed due to the reduction of copper(ii) ions (cu2+) to copper(i) oxide (cu2o). To understand the benedict's test reagent, note that it is a mixture of sodium carbonate, sodium citrate, and copper (ii) sulfate pentahydrate used to detect reducing sugars. A positive test shows a color change from blue to green, yellow, oran… The formation of a reddish precipitate within three minutes. The presence of reducing sugar in the sample. Benedict's test shows the presence of choose.reducing sugars, alcohols, amino acids. It is a qualitative chemical test that detects reducing sugars in a given sample. Examples include glucose, fructose, lactose, and maltose. The presence of the alkaline sodium carbonate con verts the sugar into a strong reducing agent. A positive benedict’s result refers to the outcome of a chemical test called the benedict’s test. A positive benedict's test appears as choose.a reddish precipitate, a blue solution ,a color. A negative test (left) and a positive test (right) Which metal is responsible for the color change in a benedict's test? A positive test shows a color change from blue to green, yellow, oran… A positive benedict’s test will cause the solution used in the test to form reddish precipitate, according to. The formation of a reddish precipitate within three minutes. A positive benedict’s result refers to the outcome of a chemical test called the benedict’s test. A positive benedict’s test will cause the solution used in the test to form reddish precipitate, according to. The presence of reducing sugar in the sample. Which metal is responsible for the color change in a benedict's test? The presence of the alkaline sodium. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like what does a positive benedict's test indicate?, what is a reducing sugar?, what solution is used to perform a benedict's test?. A positive benedict’s test is the result of the presence of reducing sugars. Benedict’ s test is performed by heating the reducing sugar solution with benedict‘s reagent. Examples include glucose,. To understand the benedict's test reagent, note that it is a mixture of sodium carbonate, sodium citrate, and copper (ii) sulfate pentahydrate used to detect reducing sugars. This precipitate is formed due to the reduction of copper(ii) ions (cu2+) to copper(i) oxide (cu2o). The benedict’s test is used to detect the presence of reducing sugars, such as. The formation of. Reducing sugars, which have a free aldehyde or. A positive benedict’s test will cause the solution used in the test to form reddish precipitate, according to. Benedict's test shows the presence of choose.reducing sugars, alcohols, amino acids. Benedict's test benedict's test is a simple biochemical reaction to detect the presence of reducing sugars. A) fructose b) glucose c) starch d). The benedict’s test is used to detect the presence of reducing sugars, such as. A positive benedict’s test will cause the solution used in the test to form reddish precipitate, according to. The presence of reducing sugar in the sample. Benedict’s test detects reducing sugars (sugars having a free reactive carbonyl group). To understand the benedict's test reagent, note that. It involves the addition of benedict’s reagent, which is a mixture of sodium. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like what does a positive benedict's test indicate?, what is a reducing sugar?, what solution is used to perform a benedict's test?. A positive benedict’s result refers to the outcome of a chemical test called the benedict’s test. These. A positive benedict's test appears as choose.a reddish precipitate, a blue solution ,a color. A positive test is indicated by: These sugars are found in. A) fructose b) glucose c) starch d) sucrose e) lactose 4. Benedict's test is used to test for simple carbohydrates, which have reducing properties. Benedict's test is used to test for simple carbohydrates, which have reducing properties. Benedict’ s test is performed by heating the reducing sugar solution with benedict‘s reagent. Reducing sugars, which have a free aldehyde or. This precipitate is formed due to the reduction of copper(ii) ions (cu2+) to copper(i) oxide (cu2o). It is a qualitative chemical test that detects reducing. Which metal is responsible for the color change in a benedict's test? Examples include glucose, fructose, lactose, and maltose. These sugars are found in. A positive benedict’s test is the result of the presence of reducing sugars. The formation of a reddish precipitate within three minutes. A positive iodine test appears as 3. Benedict's test benedict's test is a simple biochemical reaction to detect the presence of reducing sugars. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like what does a positive benedict's test indicate?, what is a reducing sugar?, what solution is used to perform a benedict's test?. Classify the following sugars as monosaccharides, disaccharide,. Benedict’s test identifies reducing sugars, which have a free aldehyde or ketone group. Benedict's test benedict's test is a simple biochemical reaction to detect the presence of reducing sugars. A positive test shows a color change from blue to green, yellow, oran… Benedict's test is used to test for simple carbohydrates, which have reducing properties. A positive iodine test appears as 3. To understand the benedict's test reagent, note that it is a mixture of sodium carbonate, sodium citrate, and copper (ii) sulfate pentahydrate used to detect reducing sugars. A positive test is indicated by: Classify the following sugars as monosaccharides, disaccharide, or polysaccharides. The benedict’s test is a method used to detect the presence of reducing sugars in a given sample. These sugars are found in. Benedict's test shows the presence of choose.reducing sugars, alcohols, amino acids. Which metal is responsible for the color change in a benedict's test? The formation of a reddish precipitate within three minutes. Benedict’ s test is performed by heating the reducing sugar solution with benedict‘s reagent. The presence of reducing sugar in the sample. Reducing sugars, which have a free aldehyde or.Benedict’s Test Principle, Procedure & Practical Uses
What Does A Positive Benedict S Test Look Like at Samuel Jones blog
PPT Chapter 13 Organic Compounds with oxygen and Sulfur PowerPoint
Benedict’s Test Principle, Procedure & Practical Uses
Benedict’s test Definition, Principle, Uses, and Reagent
What Does A Positive Benedict S Test Look Like at Samuel Jones blog
Benedict’s Test
PPT T e sting for Biological Macromolecules PowerPoint Presentation
Science experiment diagram show Benedict's test for sugar determination
PPT Biomolecules PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1800990
A Positive Benedict’s Test Will Cause The Solution Used In The Test To Form Reddish Precipitate, According To.
It Involves The Addition Of Benedict’s Reagent, Which Is A Mixture Of Sodium.
A Negative Test (Left) And A Positive Test (Right)
Benedict’s Test Detects Reducing Sugars (Sugars Having A Free Reactive Carbonyl Group).
Related Post: