Can Carbon Form Polar And Nonpolar Bonds
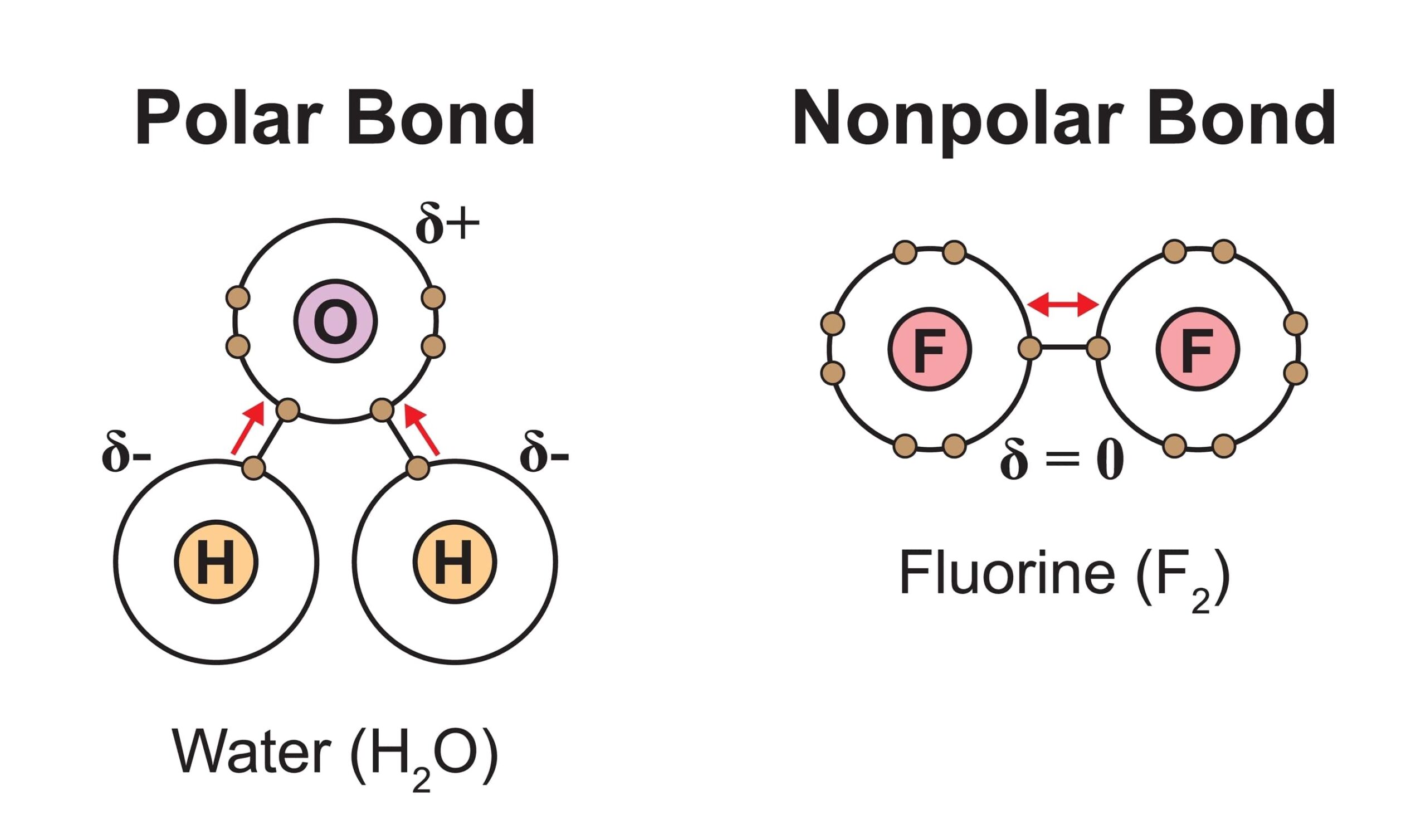
Can Carbon Form Polar And Nonpolar Bonds - Carbons are typically nice guys who like sharing their electrons with other atoms. C has an electronegativity of 2.5 and h is 2.1 for a difference of 0.4. Carbon can form both polar and nonpolar bonds. The most common type of bond formed by carbon is a covalent bond. Carbon can bond with other nonmetals such as hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen. Figure \(\pageindex{1}\) polar versus nonpolar covalent bonds. If two carbon atoms are. Carbon bonds are stable across a broad range of temperatures. Carbon can form multiple covalent bonds with other atoms. Carbon bonds are stable across a broad range of temperatures. The molecule c2 does not exist because carbon needs to form four bonds in order to achieve a full outer shell of electrons. The other type of bond we are. Carbon can bond with other nonmetals such as hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen. The two double bonds, seeking maximum separation, arrange themselves. Hydrocarbons are also molecules that have covalent. Carbon can form multiple covalent bonds with other atoms. Carbon can form both polar and nonpolar bonds. (a) the electrons in the covalent bond are equally shared by both hydrogen atoms. In most cases, carbon shares electrons with other atoms (usual valence of 4). C has an electronegativity of 2.5 and h is 2.1 for a difference of 0.4. The two double bonds, seeking maximum separation, arrange themselves. This is because carbon typically bonds with elements which have a similar electronegativity. The most common type of bond formed by carbon is a covalent bond. The nature of the bond that carbon forms with other elements depends on the electronegativity of those elements. Carbon can form multiple covalent bonds with. C has an electronegativity of 2.5 and h is 2.1 for a difference of 0.4. Carbon forms polar covalent bonds with elements that have a. Carbons are typically nice guys who like sharing their electrons with other atoms. Figure \(\pageindex{1}\) polar versus nonpolar covalent bonds. Carbon bonds are stable across a broad range of temperatures. This is because carbon typically bonds with elements which have a similar electronegativity. Carbon bonds are stable across a broad range of temperatures. Carbon can form both polar and nonpolar bonds: Carbon bonds are stable across a broad range of temperatures. The other type of bond we are. Carbon dioxide, with only bonding pairs around the central carbon atom, adopts a linear geometry. Figure \(\pageindex{1}\) polar versus nonpolar covalent bonds. No, carbon can form both polar and nonpolar covalent bonds. Carbon can form nonpolar covalent (pure covalent) bonds when it bonds to itself, as in graphene and diamond. The nature of the bond that carbon forms with other. Carbon can form nonpolar (pure covalent) covalent bonds when bonded to itself alone, as in graphene and diamond. This is because carbon typically bonds with elements which have a similar electronegativity. (a) the electrons in the covalent bond are equally shared by both hydrogen atoms. This is a nonpolar covalent. The type of bond formed depends on the electronegativity of. Carbons are typically nice guys who like sharing their electrons with other atoms. These bonds can be polar (uneven. (a) the electrons in the covalent bond are equally shared by both hydrogen atoms. Carbon typically forms covalent bonds with other atoms to achieve. Carbon forms polar covalent bonds with elements that have a. If two carbon atoms are. This is because carbon typically bonds with elements which have a similar electronegativity. C has an electronegativity of 2.5 and h is 2.1 for a difference of 0.4. Carbons are typically nice guys who like sharing their electrons with other atoms. Carbon can bond with other nonmetals such as hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen. The two double bonds, seeking maximum separation, arrange themselves. Carbon can form both polar and nonpolar bonds. Carbon can form nonpolar covalent (pure covalent) bonds when it bonds to itself, as in graphene and diamond. Carbon can form both polar and nonpolar bonds. Carbon bonds are stable across a broad range of temperatures. Carbon can form both polar and nonpolar bonds. (a) the electrons in the covalent bond are equally shared by both hydrogen atoms. Carbon can form both polar and nonpolar bonds. Carbon bonds are stable across a broad range of temperatures. The type of bond formed depends on the electronegativity of the atoms involved. Carbon can form both polar and nonpolar bonds: The nature of the bond that carbon forms with other elements depends on the electronegativity of those elements. Hydrocarbons are also molecules that have covalent. This is a nonpolar covalent. Carbon can form both polar and nonpolar bonds. Carbon forms polar covalent bonds with elements that have a. (a) the electrons in the covalent bond are equally shared by both hydrogen atoms. Carbon can bond with other nonmetals such as hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen. This is a nonpolar covalent. In most cases, carbon shares electrons with other atoms (usual valence of 4). This is because carbon typically bonds with elements which have a similar electronegativity. If two carbon atoms are. The two double bonds, seeking maximum separation, arrange themselves. The other type of bond we are. Figure \(\pageindex{1}\) polar versus nonpolar covalent bonds. The most common nonpolar covalent bonds are those between carbon and hydrogen: Carbon bonds are stable across a broad range of temperatures. Carbon can form both polar and nonpolar bonds. No, carbon can form both polar and nonpolar covalent bonds. Carbon can form both polar and nonpolar bonds: The most common type of bond formed by carbon is a covalent bond.Understanding Types of Chemical Bonds TEAS NurseHub
What Type Of Bond Is Co2 Polar Or Nonpolar Design Talk
Polar Covalent Bonds Clearly Explained for Easy Learning
Polar Covalent Bonds Clearly Explained for Easy Learning
Chapter 3 Molecules of Life ppt download
Polar Covalent Bonds Clearly Explained for Easy Learning
Polar Covalent Bonds Clearly Explained for Easy Learning
PPT Nonpolar Covalent Bonds PowerPoint Presentation, free download
Polar and Nonpolar Molecules
What is polarity? Definition from TechTarget
Carbon Dioxide, With Only Bonding Pairs Around The Central Carbon Atom, Adopts A Linear Geometry.
Carbons Are Typically Nice Guys Who Like Sharing Their Electrons With Other Atoms.
Carbon Can Form Multiple Covalent Bonds With Other Atoms.
C Has An Electronegativity Of 2.5 And H Is 2.1 For A Difference Of 0.4.
Related Post: