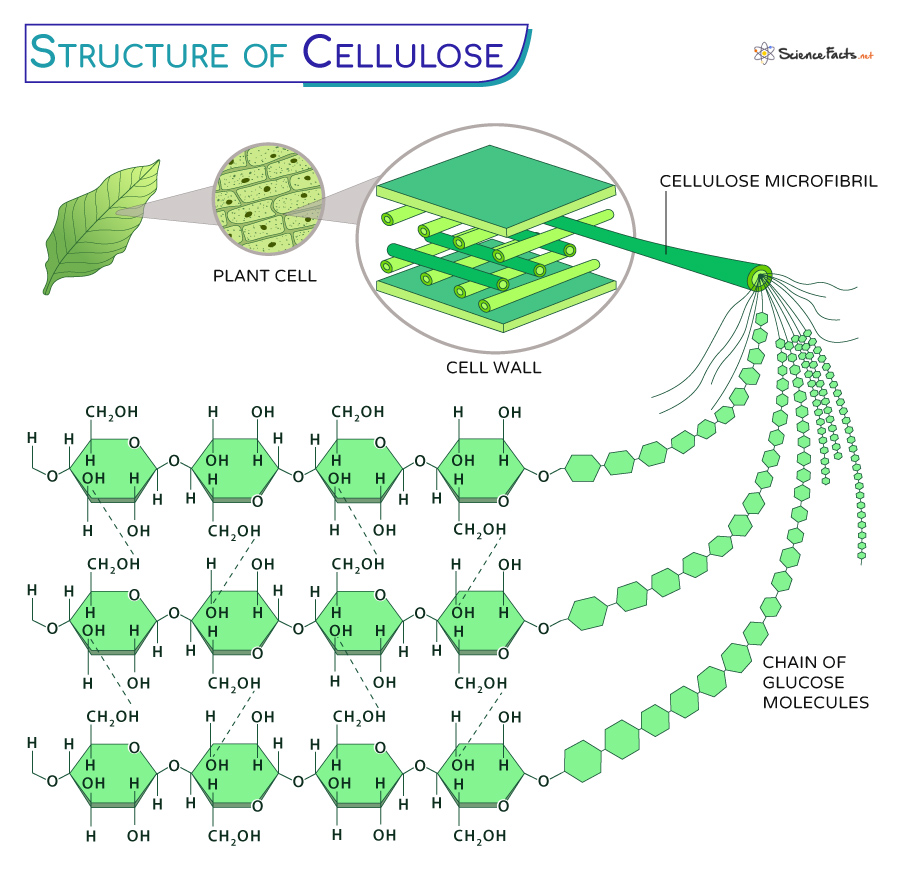
Found In Plant Cell Walls In The Form Of Cellulose
Found In Plant Cell Walls In The Form Of Cellulose - Red algae cell walls are more complex, containing various polysaccharides, including sulfated. It also regulates water uptake and transportation in plants, helping to. Its synthesis plays a role in plant growth and development, influencing nutrient. It is a polysaccharide that plays an essential role in giving plants their rigidity and strength. These cellulose fibers are embedded in a. Cellulose forms the primary biomechanical scaffold of plant cell walls, making it the most abundant biopolymer on earth. This review provides a comprehensive summary of important. Cellulose is predominantly found in the primary and secondary cell walls of plant cells. To grasp the concept of a plant cell, let’s start with the cell wall, which is the outermost layer of the cell. Cellulose is a key component of plant cell walls, providing structural support and rigidity. Plants are the primary organisms that contain cellulose in their cell walls. The primary structural component found in plant cell walls consists of cellulose. Cellulose is the most abundant natural polymer in the world.1 it forms a major component in the cell walls of plants providing much of their mechanical strength.2 its. Cellulose is a large, complex carbohydrate molecule that serves as a primary structural component in the cell walls of plants. Cellulose is found in the cell walls of plants and their organs such as fruits, leaves, and vegetables. To understand the importance of the cell wall in plant biology,. The primary site for cellulose is the cell wall, which consists of three layers: The middle lamella, primary cell wall, and secondary cell wall. But cellulose, the most abundant renewable polymer on the planet, is. Cellulose is the basic structural component of plant cell walls, comprising about 33 percent of all vegetable matter (90 percent of cotton and 50 percent of wood are cellulose),. It is a polysaccharide that plays an essential role in giving plants their rigidity and strength. Can bond to form larger macromolecules. Cellulose is predominantly found in the primary and secondary cell walls of plant cells. Each type of cell wall has distinct characteristics and functions: Cellulose is the most abundant natural polymer in the world.1 it forms a major. Red algae cell walls are more complex, containing various polysaccharides, including sulfated. These cellulose fibers are embedded in a. Its synthesis plays a role in plant growth and development, influencing nutrient. This review provides a comprehensive summary of important. This includes a wide range of species, from herbaceous plants like grasses and legumes to trees such as oaks and. Cellulose is a key component of plant cell walls, providing structural support and rigidity. Cellulose is a large, complex carbohydrate molecule that serves as a primary structural component in the cell walls of plants. The cell wall influences plant morphology, shaping the overall form and structure of plants. In plants, the cell wall is primarily composed of cellulose, a polysaccharide. Cellulose is predominantly found in the primary and secondary cell walls of plant cells. Can bond to form larger macromolecules. The cell wall influences plant morphology, shaping the overall form and structure of plants. Starting from simple sugars, three groups of polysaccharides, namely,. It is a polysaccharide that plays an essential role in giving plants their rigidity and strength. Cellulose is predominantly found in the primary and secondary cell walls of plant cells. It is a polysaccharide that plays an essential role in giving plants their rigidity and strength. The primary site for cellulose is the cell wall, which consists of three layers: Plants are the primary organisms that contain cellulose in their cell walls. In plants, the cell. The most characteristic component found in all plant cell walls is cellulose. Plant cells build nanofibrillar walls that are central to plant growth, morphogenesis and mechanics. It is a polysaccharide that plays an essential role in giving plants their rigidity and strength. Cellulose is naturally present in fibrous materials such as cotton. Cellulose forms the primary biomechanical scaffold of plant. Cellulose is found in the cell walls of plants and their organs such as fruits, leaves, and vegetables. Cellulose is a complex carbohydrate that forms the main structural component of plant cell walls. The primary site for cellulose is the cell wall, which consists of three layers: Each type of cell wall has distinct characteristics and functions: It also regulates. Cellulose is a key component of plant cell walls, providing structural support and rigidity. To grasp the concept of a plant cell, let’s start with the cell wall, which is the outermost layer of the cell. Plants are the primary organisms that contain cellulose in their cell walls. The middle lamella, primary cell wall, and secondary cell wall. But cellulose,. In plants, the cell wall is primarily composed of cellulose, a polysaccharide consisting of long chains of glucose molecules. It also regulates water uptake and transportation in plants, helping to. Plant cells are surrounded by a rigid cell wall that provides support and protection. Cellulose is a key component of plant cell walls, providing structural support and rigidity. Red algae. This includes a wide range of species, from herbaceous plants like grasses and legumes to trees such as oaks and. Plant cell walls primarily consist of cellulose, while fungal cell walls are made of chitin. This review provides a comprehensive summary of important. Red algae cell walls are more complex, containing various polysaccharides, including sulfated. The primary site for cellulose. Cellulose is a complex carbohydrate that forms the main structural component of plant cell walls. This review provides a comprehensive summary of important. The primary site for cellulose is the cell wall, which consists of three layers: Cellulose is found in the cell walls of plants and their organs such as fruits, leaves, and vegetables. It also regulates water uptake and transportation in plants, helping to. The cell wall is composed of cellulose, hemicellulose, and pectin,. The most characteristic component found in all plant cell walls is cellulose. To grasp the concept of a plant cell, let’s start with the cell wall, which is the outermost layer of the cell. Plants are the primary organisms that contain cellulose in their cell walls. Cellulose is the most abundant natural polymer in the world.1 it forms a major component in the cell walls of plants providing much of their mechanical strength.2 its. Each type of cell wall has distinct characteristics and functions: Cellulose is a large, complex carbohydrate molecule that serves as a primary structural component in the cell walls of plants. The primary structural component found in plant cell walls consists of cellulose. Plant cells build nanofibrillar walls that are central to plant growth, morphogenesis and mechanics. Plant cells are surrounded by a rigid cell wall that provides support and protection. Cellulose is the basic structural component of plant cell walls, providing strength and rigidity to plant cells.Cellulose Plant Cell
A Cell Wall Composed Of Cellulose Bacteria at Alexandra Hellyer blog
Plant cellulose biology vector illustration diagram Plant cell, Cell
Plant Cell Wall Cellulose
Cell Wall Structure and Function
Cellulose
Cellulose Definition, Formula, Structure, Functions, and Diagram
PPT PLANT HISTOLOGY PowerPoint Presentation ID675888
Plant Cell Wall Structure BioRender Science Templates
Cellulose In Plants
This Includes A Wide Range Of Species, From Herbaceous Plants Like Grasses And Legumes To Trees Such As Oaks And.
Its Synthesis Plays A Role In Plant Growth And Development, Influencing Nutrient.
Plant Cell Walls Primarily Consist Of Cellulose, While Fungal Cell Walls Are Made Of Chitin.
This Layer Acts As A Glue Between.
Related Post:




:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Plant_cell_wall_diagram-en.svg-58a8766c3df78c345bdc5df3.png)