Structures That Form An Enclosure For The Spinal Cord
Structures That Form An Enclosure For The Spinal Cord - The long, tubular space within the vertebral column that. The structures that form an enclosure for the spinal cord include the vertebral column, or** backbone**, as well as certain membranes called meninges. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like vertebral type containing foramina in the transverse processes, through which the vertebral arteries ascend to reach the. In this article, we will discuss the differences between. We review gross and structural features of the spinal cord, its coverings, and nerves while also discussing spinal cord development, microscopic organization, and common. Describe how a spinal nerve exits from the vertebral column. There are three main causes of tethered spinal cord syndrome:. The spine is divided into the cervical spine (neck), the thoracic spine (chest & ribs), lumbar spine (lower back) anc coccyx, or tailbone. The sacrum and coccyx, fused vertebrae at the base, complete. These are small openings between every pair of vertebrae through which nerve roots exit the spinal cord. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like vertebral foramen, body, spinous, transverse. These two structures, namely, the posterior root and the sensory ganglia are the sensory part of the spinal nerve, meaning that they carry information towards the spinal cord. The structures that form an enclosure for the spinal cord include the vertebral column, or** backbone**, as well as certain membranes called meninges. We review gross and structural features of the spinal cord, its coverings, and nerves while also discussing spinal cord development, microscopic organization, and common. The spinal cord is a tubular structure composed of nervous tissue that extends from the brainstem and continues distally before tapering at the lower thoracic/upper lumbar. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like vertebral type containing foramina in the transverse processes, through which the vertebral arteries ascend to reach the. The long, tubular space within the vertebral column that. In this article, we will discuss the differences between. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like vertebral foramen, body, spinous and transverse process and more. Directly lining the spinal cord is the pia mater, which also thickens to form the denticulate ligament, anchoring the spinal cord in the middle of the vertebral canal. These two structures, namely, the posterior root and the sensory ganglia are the sensory part of the spinal nerve, meaning that they carry information towards the spinal cord. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like vertebral foramen, body, spinous and transverse process and more. Tethered cord happens when the spinal cord gets stuck to tissue around it, instead. These two structures, namely, the posterior root and the sensory ganglia are the sensory part of the spinal nerve, meaning that they carry information towards the spinal cord. There are three main causes of tethered spinal cord syndrome:. Directly lining the spinal cord is the pia mater, which also thickens to form the denticulate ligament, anchoring the spinal cord in. Directly lining the spinal cord is the pia mater, which also thickens to form the denticulate ligament, anchoring the spinal cord in the middle of the vertebral canal. In this article, we will discuss the differences between. The structures that form an enclosure for the spinal cord include the vertebral column, or** backbone**, as well as certain membranes called meninges.. The spinal cord is part of the central nervous system (cns), which extends caudally and is protected by the bony structures of the vertebral column. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like vertebral foramen, body, spinous, transverse. The spinal cord is a conduit for sensory nerves travelling toward the brain and motor nerves travelling from the brain. There. The spine is divided into the cervical spine (neck), the thoracic spine (chest & ribs), lumbar spine (lower back) anc coccyx, or tailbone. Three layers of tissue protect the spinal cord: The structures that form an enclosure for the spinal cord include the vertebral column, or** backbone**, as well as certain membranes called meninges. The spinal cord is a tubelike. In this article, we will discuss the differences between. Directly lining the spinal cord is the pia mater, which also thickens to form the denticulate ligament, anchoring the spinal cord in the middle of the vertebral canal. The spinal cord is a tubelike structure that consists of a bundle of nerves that extends from the base of the brain and. There are three main causes of tethered spinal cord syndrome:. In this article, we will discuss the differences between. The boney structures are the vertebral foramina. Directly lining the spinal cord is the pia mater, which also thickens to form the denticulate ligament, anchoring the spinal cord in the middle of the vertebral canal. The spinal cord carries messages from. The dura mater, arachnoid mater, and pia mater. These two structures, namely, the posterior root and the sensory ganglia are the sensory part of the spinal nerve, meaning that they carry information towards the spinal cord. It is covered by the. The boney structures are the vertebral foramina. The structures that form an enclosure for the spinal cord include the. Three layers of tissue protect the spinal cord: There are three main causes of tethered spinal cord syndrome:. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like vertebral foramen, body, spinous, transverse. Tethered cord happens when the spinal cord gets stuck to tissue around it, instead of floating freely within the spinal canal. The sacrum and coccyx, fused vertebrae at. The spinal cord is a conduit for sensory nerves travelling toward the brain and motor nerves travelling from the brain. The dura mater, arachnoid mater, and pia mater. The long, tubular space within the vertebral column that. The spinal cord is a tubular structure composed of nervous tissue that extends from the brainstem and continues distally before tapering at the. Three layers of tissue protect the spinal cord: Doctors call these layers “meninges.” the layers are as follows: The long, tubular space within the vertebral column that. The structures that form an enclosure for the spinal cord include the vertebral column, or** backbone**, as well as certain membranes called meninges. These two structures, namely, the posterior root and the sensory ganglia are the sensory part of the spinal nerve, meaning that they carry information towards the spinal cord. Structures that form an enclosure for the spinal cord. The spinal cord carries messages from the brain to the. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like vertebral foramen, body, spinous, transverse. There are three main causes of tethered spinal cord syndrome:. Spinal nerves ( motor axons) exit the vertebral column via the ventral root. It is covered by the. We review gross and structural features of the spinal cord, its coverings, and nerves while also discussing spinal cord development, microscopic organization, and common. The spinal cord is a conduit for sensory nerves travelling toward the brain and motor nerves travelling from the brain. There are 7 cervical vertebrae in the neck, 12 thoracic vertebrae in the upper back, and 5 lumbar vertebrae in the lower back. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like vertebral foramen, body, spinous and transverse process and more. The boney structures are the vertebral foramina.The structure of the spinal cord. Infographics. Vector illustration on
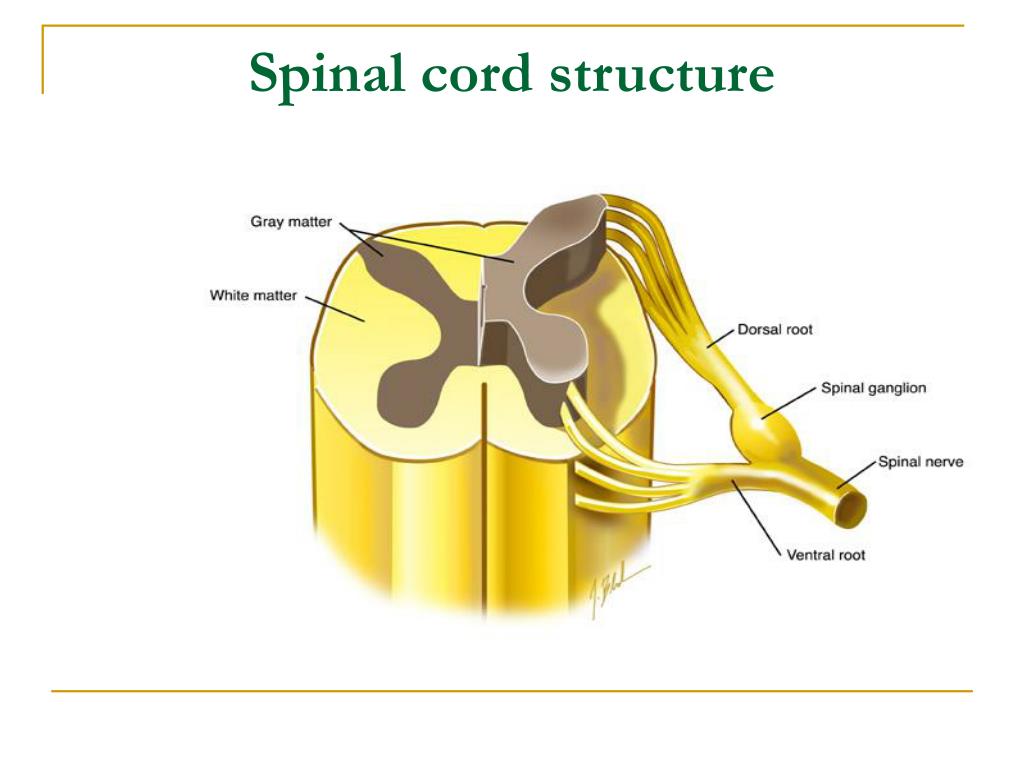
Spinal Cord
Spinal cord Anatomy, structure, tracts and function Kenhub
Spinal Cord Structure Identification Diagram Quizlet
PPT The Spinal Cord & Spinal Nerves PowerPoint Presentation ID1772226
PPT Spinal Cord lesions PowerPoint Presentation ID407568
Spinal cord structure diagram medical science Vector Image
Spinal cord anatomy Physiopedia
Ch.14 Spinal Cord Structures (pt.1) Diagram Quizlet
I Anatomy II Physiology Spinal Cord 1 The
Study With Quizlet And Memorize Flashcards Containing Terms Like Vertebral Type Containing Foramina In The Transverse Processes, Through Which The Vertebral Arteries Ascend To Reach The.
These Are Small Openings Between Every Pair Of Vertebrae Through Which Nerve Roots Exit The Spinal Cord.
The Dura Mater, Arachnoid Mater, And Pia Mater.
The Spinal Cord Is A Tubular Structure Composed Of Nervous Tissue That Extends From The Brainstem And Continues Distally Before Tapering At The Lower Thoracic/Upper Lumbar.
Related Post:


:watermark(/images/watermark_5000_10percent.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/overview_image/456/SwztiC2MdqeIOymo5rPJZg_spinal-membranes-and-nerve-roots_english.jpg)