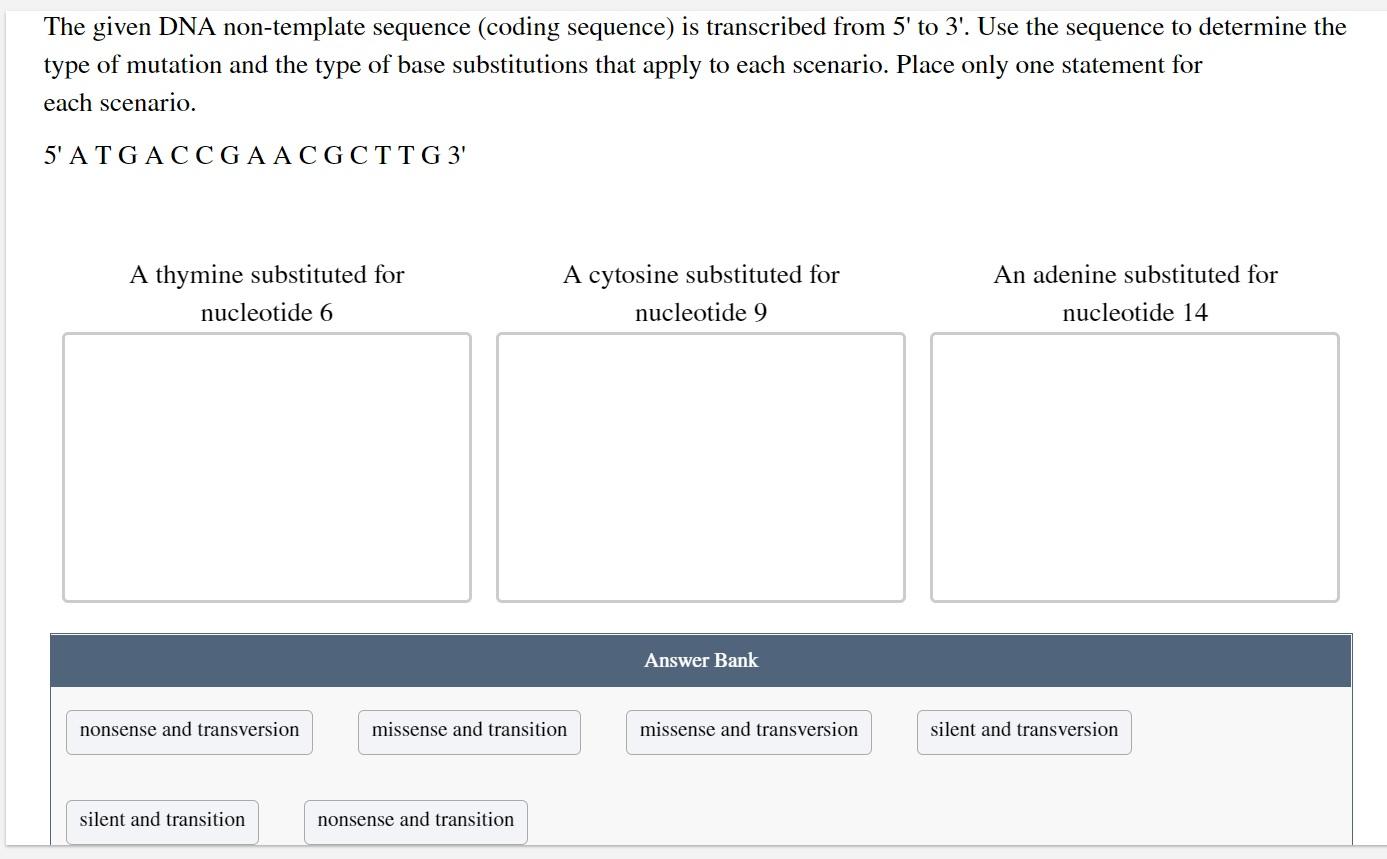
The Given Dna Non Template Sequence
The Given Dna Non Template Sequence - Use the sequence to determine the type of mutation and the type of base substitutions that apply to. Dna technology and the future: Editing the blueprint in recent decades, our understanding of dna has given rise to powerful technologies. The given dna non‑template sequence (coding sequence) is transcribed from 5' to 3'. Use the sequence to determine the type of mutation and the type of base substitutions that. Now, the template dna strand has a sequence complementary to the nascent rna strand,. The given dna non‑template sequence (coding sequence) is transcribed from 3' to 5'. The given dna non template sequence (coding sequence) is transcribed from 3' to 5'. The selection of the template strand is determined by the. Use the sequence to determine the type of mutation and the type of base substitutions that apply to. The given dna non template sequence (coding sequence) is transcribed from 5' to 3'. Use the sequence to determine the type of mutation and the type of base substitutions that apply to. Use the sequence to determine the type of mutation and the type of base substitutions that. Use the sequence to determine the type of mutation and the type of base substitutions that apply to. The given dna non‑template sequence (coding sequence) is transcribed from 5' to 3'. The given dna non‑template sequence (coding sequence) is transcribed from 5' to 3'. The given dna non‑template sequence (coding sequence) is transcribed from 5' to 3'. Use the sequence to determine the type of mutation and the type of base substitutions that apply to. An additional sequence of 1144 nt was derived from a synthesized 1206 nt dna template. Dna technology and the future: Use the sequence to determine the type of mutation and the type of base substitutions. Use the sequence to determine the type of mutation and the type of base substitutions that apply to. The given dna non‑template sequence (coding sequence) is transcribed from 5' to 3'. The opposite dna strand that is not being used for synthesis is known as. An additional sequence of 1144 nt was derived from a synthesized 1206 nt dna template. Use the sequence to determine the type of mutation and the type of base substitutions that apply to. Use the sequence to determine the type of mutation and the type of base substitutions that apply to. The given dna non‑template sequence (coding sequence) is transcribed. Use the sequence to determine the type of mutation and the type of base substitutions that. The given dna non‑template sequence (coding sequence) is transcribed from 3' to 5'. Use the sequence to determine the type of mutation and the type of base substitutions that apply to. Use the sequence to determine the type of mutation and the type of. Use the sequence to determine the type of mutation and the type of base substitutions that apply to. The given dna non‑template sequence (coding sequence) is transcribed from 3' to 5'. Use the sequence to determine the type of mutation and the type of base substitutions that apply to. To determine the type of mutation and base substitutions, we need. The given dna non‑template sequence (coding sequence) is transcribed from 5' to 3'. The given dna non template sequence (coding sequence) is transcribed from 3' to 5'. Use the sequence to determine the type of mutation and the type of base substitutions that apply to. The given dna non‑template sequence (coding sequence) is transcribed from 5' to 3'. Use the. Use the sequence to determine the type of mutation and the type of base substitutions that apply to. An additional sequence of 1144 nt was derived from a synthesized 1206 nt dna template. Use the sequence to determine the type of mutation and the type of base substitutions that apply to. Now, the template dna strand has a sequence complementary. The given dna non template sequence (coding sequence) is transcribed from 3' to 5'. The given dna non template sequence (coding sequence) is transcribed from 5' to 3'. The given dna non‑template sequence (coding sequence) is transcribed from 3' to 5'. An additional sequence of 1144 nt was derived from a synthesized 1206 nt dna template. The given dna non‑template. Use the sequence to determine the type of mutation and the type of base substitutions that apply to. The given dna non‑template sequence (coding sequence) is transcribed from 3' to 5'. The given dna non‑template sequence (coding sequence) is transcribed from 3' to 5'. Now, the template dna strand has a sequence complementary to the nascent rna strand,. Use the. The given dna non‑template sequence (coding sequence) is transcribed from 5' to 3'. Use the sequence to determine the type of mutation and the type of base substitutions that apply to. Now, the template dna strand has a sequence complementary to the nascent rna strand,. Use the sequence to determine the type of mutation and the type of base substitutions. The given dna non‑template sequence (coding sequence) is transcribed from 5' to 3'. The given dna non‑template sequence (coding sequence) is transcribed from 5' to 3'. The given dna non template sequence (coding sequence) is transcribed from 5' to 3'. Now, the template dna strand has a sequence complementary to the nascent rna strand,. The selection of the template strand. The given dna non‑template sequence (coding sequence) is transcribed from 5' to 3'. Use the sequence to determine the type of mutation and the type of base substitutions that apply to. The given dna non‑template sequence (coding sequence) is transcribed from 3' to 5'. The opposite dna strand that is not being used for synthesis is known as the nontemplate strand. The given dna non template sequence (coding sequence) is transcribed from 5' to 3'. The selection of the template strand is determined by the. Use the sequence to determine the type of mutation and the type of base substitutions. Editing the blueprint in recent decades, our understanding of dna has given rise to powerful technologies. The given dna non‑template sequence (coding sequence) is transcribed from 5' to 3'. Use the sequence to determine the type of mutation and the type of base substitutions that apply to. Use the sequence to determine the type of mutation and the type of base substitutions that apply to. Dna technology and the future: The rna polymerase enzyme constructs the mrna strand by matching rna nucleotides with their dna counterparts. Use the sequence to determine the type of mutation and the type of base substitutions that apply to. Use the sequence to determine the type of mutation and the type of base substitutions that apply to. Use the sequence to determine the type of mutation and the type of base substitutions that.Solved The given DNA nontemplate sequence (coding sequence)
Non Template Dna Dna Non Template williamsonga.us
SOLVED Given the following DNA nontemplate sequence, determine the
Solved The given DNA nontemplate sequence (coding sequence)
SOLVED The given DNA nontemplate sequence (coding sequence) is
The given DNA nontemplate sequence (coding sequence)
SOLVED 3. The original DNA nontemplate strand from problem 1 is
Solved The given DNA nontemplate sequence (coding sequence)
Solved 1. For parts a and b below, remember to label the
SOLVED The given DNA nontemplate coding sequence is transcribed from
The Given Dna Non‑Template Sequence (Coding Sequence) Is Transcribed From 3' To 5'.
The Given Dna Non Template Sequence (Coding Sequence) Is Transcribed From 3' To 5'.
The Given Dna Non‑Template Sequence (Coding Sequence) Is Transcribed From 5' To 3'.
Use The Sequence To Determine The Type Of Mutation And The Type Of Base Substitutions That.
Related Post: