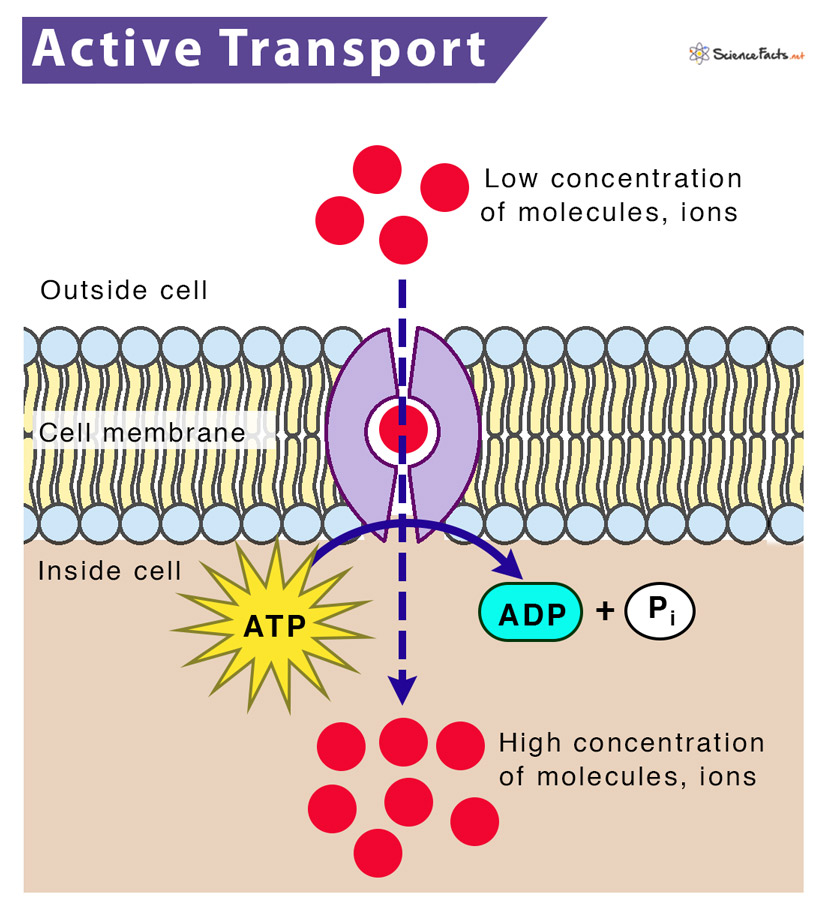
Which Of The Following Is A Form Of Active Transport
Which Of The Following Is A Form Of Active Transport - Which of the following processes is an example of active transport? In active transport, energy (atp) is used to move substances down. The oxygen concentration in the. An example of active transport. Active transport is a type of transport that involves the movement of molecules or ions from an area of lower concentration to an area of higher concentration, against their. Active transport is a process that moves molecules across a cell membrane from a region of lower concentration to a region of higher concentration, using energy. The primary active transport system uses atp to move a substance,. Unlike passive processes like simple diffusion. This process ensures that cells maintain necessary. It occurs against the concentration gradient. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like which of the following is not a characteristic of active transport: The oxygen concentration in the. An example of active transport. In active transport, energy (atp) is used to move substances down. Active transport involves using energy from atp to transport substances across the cell membrane against their concentration gradients. The primary active transport system uses atp to move a substance,. Bulk passage is a form of active transport because it involves the movement of large molecules or particles across the cell membrane, which requires energy. It occurs against the concentration gradient. In this case, glucose is moving from an area of low. These form part of the sites on the outside of the cell that allow it to be recognized by and interact with other cells. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like which of the following is not a characteristic of active transport: In active transport, energy (atp) is used to move substances down. Active transport is the movement of solutes from low to high concentration across a membrane using energy, usually atp. Unlike passive processes like simple diffusion. Active transport describes the. These form part of the sites on the outside of the cell that allow it to be recognized by and interact with other cells. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like which of the following is not a characteristic of active transport: Passive transport is when substances move across the cell membrane. Unlike passive processes like simple diffusion.. In active transport, energy (atp) is used to move substances down. Active transport describes the shuttling of anions into the nucleus to produce atp. The oxygen concentration in the. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like which of the following is not a characteristic of active transport: Primary active transport moves ions across a membrane and creates a. Active transport involves using energy from atp to transport substances across the cell membrane against their concentration gradients. During cell respiration, the reactants of glucose and oxygen are transformed into the. In active transport, energy (atp) is used to move substances down. Active transport describes the shuttling of anions into the nucleus to produce atp. Bulk passage is a form. Primary active transport moves ions across a membrane and creates a difference in charge across that membrane. This process ensures that cells maintain necessary. Which of the following is a characteristic of active transport? Active transport is a process that moves molecules or ions against their concentration gradient (from an area of lower concentration to an area of higher concentration).. Active transport is a process that moves molecules or ions against their concentration gradient (from an area of lower concentration to an area of higher concentration). During cell respiration, the reactants of glucose and oxygen are transformed into the. Active transport describes the shuttling of anions into the nucleus to produce atp. This process ensures that cells maintain necessary. Active. Active transport describes the shuttling of anions into the nucleus to produce atp. Which of the following is a characteristic of active transport? Passive transport is when substances move across the cell membrane. During cell respiration, the reactants of glucose and oxygen are transformed into the. In this case, glucose is moving from an area of low. Active transport is the movement of solutes from low to high concentration across a membrane using energy, usually atp. In this case, glucose is moving from an area of low. Passive transport is when substances move across the cell membrane. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like which of the following is not a characteristic of active transport:. Active transport is a process that moves molecules across a cell membrane from a region of lower concentration to a region of higher concentration, using energy. Active transport is a process that moves molecules or ions against their concentration gradient (from an area of lower concentration to an area of higher concentration). Active transport is the movement of solutes from. In active transport, energy (atp) is used to move substances down. Active transport is the movement of solutes from low to high concentration across a membrane using energy, usually atp. Bulk passage is a form of active transport because it involves the movement of large molecules or particles across the cell membrane, which requires energy. Unlike passive processes like simple. In this case, glucose is moving from an area of low. Passive transport is when substances move across the cell membrane. Active transport is a type of transport that involves the movement of molecules or ions from an area of lower concentration to an area of higher concentration, against their. Bulk passage is a form of active transport because it involves the movement of large molecules or particles across the cell membrane, which requires energy. Primary active transport moves ions across a membrane and creates a difference in charge across that membrane. Active transport is a process that moves molecules or ions against their concentration gradient (from an area of lower concentration to an area of higher concentration). During cell respiration, the reactants of glucose and oxygen are transformed into the. It occurs against the concentration gradient. Exocytosis is a form of active transport. Unlike passive processes like simple diffusion. This process ensures that cells maintain necessary. Active transport describes the shuttling of anions into the nucleus to produce atp. Active transport is a process that moves molecules across a cell membrane from a region of lower concentration to a region of higher concentration, using energy. These form part of the sites on the outside of the cell that allow it to be recognized by and interact with other cells. The oxygen concentration in the. Active transport involves using energy from atp to transport substances across the cell membrane against their concentration gradients.Examples Of Transport Definition Biology at Daniel Nielsen blog
Active Transport In Plants
Types of active transport hires stock photography and images Alamy
Active transport AQA GCSE Biology Revision Notes 2016
Active Transport
Active Transport Tutorial Sophia Learning
Active Transport GCSE Biology Revision
Active Transport Definition, Types, Functions and Diagram
Active Transport
Which Is A Active Transport Process Printable Templates Protal
Study With Quizlet And Memorize Flashcards Containing Terms Like Which Of The Following Is Not A Characteristic Of Active Transport:
In Active Transport, Energy (Atp) Is Used To Move Substances Down.
An Example Of Active Transport.
Which Of The Following Is True Regarding Active Transport?
Related Post: